Difference between revisions of "Introduction/Landing/Malocclusion Rethought"
| (32 intermediate revisions by the same user not shown) | |||
| Line 2: | Line 2: | ||
{{DISPLAYTITLE: Malocclusion Rethought — Occlusal Dysmorphisms}} | {{DISPLAYTITLE: Malocclusion Rethought — Occlusal Dysmorphisms}} | ||
<!-- HERO | <!-- HERO --> | ||
<div style="background:#f2f7ff; border-radius:14px; padding:28px; text-align:center; margin-bottom:22px | <div style="background:#f2f7ff; border-radius:14px; padding:28px; text-align:center; margin-bottom:22px;"> | ||
<h1 style="margin:.2rem 0; font-size:2.2rem; line-height:1.2;">Malocclusion Rethought</h1> | <h1 style="margin:.2rem 0; font-size:2.2rem; line-height:1.2;">Malocclusion Rethought</h1> | ||
<p style="font-size:1.08rem; opacity:.85; margin:.5rem 0 1.2rem;"> | <p style="font-size:1.08rem; opacity:.85; margin:.5rem 0 1.2rem;"> | ||
From | From “Malocclusion” to a broader paradigm: <b>Occlusal Dysmorphisms</b>. | ||
</p> | </p> | ||
< | <span class="mw-ui-button mw-ui-progressive" style="border-radius:9999px; background:linear-gradient(90deg,#5b86ff,#36d1dc); box-shadow:0 2px 8px rgba(0,0,0,.15); font-weight:600; padding:10px 22px;"> | ||
[https://www.masticationpedia.org/index.php/Introduction 👉 Read the full chapter] | |||
</ | </span> | ||
</div> | </div> | ||
< | == Malocclusion Rethought == | ||
< | |||
The term "Malocclusion," derived from the Latin ''malum'' ("bad"), was first introduced by Edward Angle to define an improper “closure” of teeth.<ref>Attributed to [[:wpen:Edward Angle|Edward Angle]], the father of modern orthodontics.</ref> Yet, the notion of "bad closure" remains ambiguous in medical contexts. | |||
A PubMed search for "Malocclusion" yields over 33,000 articles,<ref>Pubmed, ''[https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/?term=%22malocclusion%22 Malocclusion]''</ref> but without clear consensus on its definition. Smaglyuk et al. stress the importance of an interdisciplinary approach in diagnostics,<ref>{{cita libro | |||
| autore = Smaglyuk LV | |||
</ | | autore2 = Voronkova HV | ||
| autore3 = Karasiunok AY | |||
| autore4 = Liakhovska AV | |||
| autore5 = Solovei KO | |||
| titolo = Interdisciplinary approach to diagnostics of malocclusions (review) | |||
| url = https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/31175796 | |||
| opera = Wiad Lek | |||
| anno = 2019 | |||
}} 72(5 cz 1):918-922.</ref> yet a query for "interdisciplinary diagnostics of malocclusions" returns only four articles,<ref>Pubmed, ''[https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/?term=interdisciplinary+diagnostics+of+malocclusions Interdisciplinary diagnostics of malocclusions]''</ref> underscoring a major gap in the literature. This suggests a paradigmatic shift may be underway, as described in Kuhn’s phase 4 model. | |||
{{q2|Diagnosis, treatment strategies, and prevention of anomalies and dento-facial deformities should consider the organism as a whole, particularly in children whose structures are still developing.}} | |||
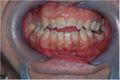
A clinical case illustrates this complexity: a patient presented with a unilateral posterior crossbite and anterior open bite. Literature suggests orthodontic appliances and sometimes orthognathic surgery are indicated.<ref>{{cita libro | |||
| autore = Reichert I | |||
| autore2 = Figel P | |||
| autore3 = Winchester L | |||
| titolo = Orthodontic treatment of anterior open bite: a review article--is surgery always necessary? | |||
| url = https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/23949448 | |||
| opera = Oral Maxillofac Surg | |||
| anno = 2014 | |||
}} Sep;18(3):271-7.</ref> Crossbite correction is equally important due to its functional link with open bite.<ref>{{cita libro | |||
| autore = Miamoto CB | |||
| autore2 = Silva Marques L | |||
| autore3 = Abreu LG | |||
| autore4 = Paiva SM | |||
| titolo = Impact of two early treatment protocols for anterior dental crossbite on children’s quality of life | |||
| url = https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC5962250/pdf/2176-9451-dpjo-23-01-00071.pdf | |||
| opera = Dental Press J Orthod | |||
| anno = 2018 | |||
}} Jan-Feb; 23(1) 71–78.</ref> In this case, however, the patient refused treatment, claiming function was unaffected. | |||
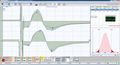
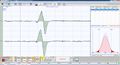
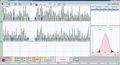
Electrophysiological testing revealed functional symmetry in the masticatory system despite occlusal discrepancies. Findings included: | |||
<gallery mode="slideshow"> | |||
File:Occlusal Centric view in open and cross bite patient.jpg|'''Figure 1a:''' Malocclusion with open bite and right posterior crossbite. | |||
File:Bilateral Electric Transcranial Stimulation.jpg|'''Figure 1b:''' Motor-evoked potential symmetry in masseter muscles. | |||
File:Jaw Jerk .jpg|'''Figure 1c:''' Jaw reflex test confirming functional balance. | |||
File:Mechanic Silent Period.jpg|'''Figure 1d:''' Mechanical silent period indicating neuromuscular coherence. | |||
</gallery> | |||
These results challenge the reductionist view of malocclusion, showing that **neuromuscular balance may coexist with occlusal asymmetries**. Hence, diagnostic strategies must integrate occlusion with neurophysiology to avoid oversimplification. | |||
< | <blockquote>''Occlusal Dysmorphisms, not simply Malocclusion — an entirely different paradigm.''</blockquote> | ||
</ | |||
{{Bib}} | |||
<!-- CTA | <!-- CTA finale --> | ||
<!-- CTA finale --> | |||
<div style="text-align:center; margin:34px 0 8px;"> | <div style="text-align:center; margin:34px 0 8px;"> | ||
<span class=" | <span class="mw-ui-button mw-ui-progressive" | ||
[https://www.masticationpedia.org/index.php/ | style="border-radius:9999px; background:linear-gradient(90deg,#5b86ff,#36d1dc); | ||
box-shadow:0 2px 8px rgba(0,0,0,.15); font-weight:600; padding:10px 22px; color:#fff;"> | |||
[https://www.masticationpedia.org/index.php/Introduction#Dental_Malocclusion 👉 Explore the full section in the Introduction] | |||
</span> | </span> | ||
</div> | </div> | ||
Latest revision as of 18:24, 19 September 2025
Malocclusion Rethought
From “Malocclusion” to a broader paradigm: Occlusal Dysmorphisms.
Malocclusion Rethought
The term "Malocclusion," derived from the Latin malum ("bad"), was first introduced by Edward Angle to define an improper “closure” of teeth.[1] Yet, the notion of "bad closure" remains ambiguous in medical contexts.
A PubMed search for "Malocclusion" yields over 33,000 articles,[2] but without clear consensus on its definition. Smaglyuk et al. stress the importance of an interdisciplinary approach in diagnostics,[3] yet a query for "interdisciplinary diagnostics of malocclusions" returns only four articles,[4] underscoring a major gap in the literature. This suggests a paradigmatic shift may be underway, as described in Kuhn’s phase 4 model.
A clinical case illustrates this complexity: a patient presented with a unilateral posterior crossbite and anterior open bite. Literature suggests orthodontic appliances and sometimes orthognathic surgery are indicated.[5] Crossbite correction is equally important due to its functional link with open bite.[6] In this case, however, the patient refused treatment, claiming function was unaffected.
Electrophysiological testing revealed functional symmetry in the masticatory system despite occlusal discrepancies. Findings included:
These results challenge the reductionist view of malocclusion, showing that **neuromuscular balance may coexist with occlusal asymmetries**. Hence, diagnostic strategies must integrate occlusion with neurophysiology to avoid oversimplification.
Occlusal Dysmorphisms, not simply Malocclusion — an entirely different paradigm.
- ↑ Attributed to Edward Angle, the father of modern orthodontics.
- ↑ Pubmed, Malocclusion
- ↑ Smaglyuk LV, Voronkova HV, Karasiunok AY, Liakhovska AV, Solovei KO, «Interdisciplinary approach to diagnostics of malocclusions (review)», in Wiad Lek, 2019». 72(5 cz 1):918-922.
- ↑ Pubmed, Interdisciplinary diagnostics of malocclusions
- ↑ Reichert I, Figel P, Winchester L, «Orthodontic treatment of anterior open bite: a review article--is surgery always necessary?», in Oral Maxillofac Surg, 2014». Sep;18(3):271-7.
- ↑ Miamoto CB, Silva Marques L, Abreu LG, Paiva SM, «Impact of two early treatment protocols for anterior dental crossbite on children’s quality of life», in Dental Press J Orthod, 2018». Jan-Feb; 23(1) 71–78.