Difference between revisions of "The logic of probabilistic language"
(Created page with "{{Bookind2}} <languages /> alt=|left|250x250px <translate><!--T:1--> In this chapter, we will discuss the logic of language coupled with mathematical probability</translate>. <translate><!--T:2--> We have seen that classical logic alone is insufficient to determine accurate diagnoses</translate>; <translate><!--T:3--> hence, a conceptual and formal overview is given on why probability can be ver...") |
Gianfranco (talk | contribs) |
||
| (20 intermediate revisions by 3 users not shown) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
<languages /> | <languages /> | ||
[[File:Spasmo_emimasticatorio_JJ.jpg|alt=|left|250x250px]] | [[File:Spasmo_emimasticatorio_JJ.jpg|alt=|left|250x250px]] | ||
<translate><!--T:1--> In this chapter, we will discuss the logic of language coupled with mathematical probability</translate>. <translate><!--T:2--> We have seen that [[The logic of classical language|classical logic]] alone is insufficient to determine accurate diagnoses</translate>; <translate><!--T:3--> hence, a conceptual and formal overview is given on why probability can be very useful</translate>. <translate><!--T:4--> Providing illustrations of instances of clinical cases, we will see how the logic of probabilistic language is able to provide us a differential diagnosis in a ‘good enough’ way</translate>. | <translate><!--T:1--> In this chapter, we will discuss the logic of language coupled with mathematical probability</translate>. <translate><!--T:2--> We have seen that [[The logic of classical language|classical logic]] alone is insufficient to determine accurate diagnoses</translate>; <translate><!--T:3--> hence, a conceptual and formal overview is given on why probability can be very useful</translate>. <translate><!--T:4--> Providing illustrations of instances of clinical cases, we will see how the logic of probabilistic language is able to provide us a differential diagnosis in a ‘good enough’ way</translate>. | ||
| Line 13: | Line 14: | ||
| autore3 = Flavio Frisardi | | autore3 = Flavio Frisardi | ||
}} | }} | ||
{{Bookind2}} | |||
==<translate><!--T:6--> Probabilistic language logic in medicine</translate>== | ==<translate><!--T:6--> Probabilistic language logic in medicine</translate>== | ||
<translate><!--T:7--> | <translate><!--T:7--> every scientific idea (whether in medicine, architecture, engineering, chemistry, or any other subject), when put into practice, is subject to small errors and uncertainties</translate>. <translate><!--T:8--> Mathematics - through probability theory and statistical inference - helps to precisely control and thereby contain these uncertainties</translate>. <translate><!--T:9--> It always has to be considered that in all practical cases "the outcomes also depend on many other factors external to the theory", whether they be initial and environmental conditions, experimental errors, or something else</translate>. | ||
<translate><!--T:10--> All the uncertainties about these factors make the theory–observation relationship a probabilistic one</translate>. <translate><!--T:11--> In the medical approach, there are two types of uncertainty that weigh the most on diagnoses: subjective uncertainty and casuality</translate>.<ref>{{Cite book | <translate><!--T:10--> All the uncertainties about these factors make the theory–observation relationship a probabilistic one</translate>. <translate><!--T:11--> In the medical approach, there are two types of uncertainty that weigh the most on diagnoses: subjective uncertainty and casuality</translate>.<ref>{{Cite book | ||
| Line 182: | Line 184: | ||
:*<math>cr>0</math> <translate><!--T:77--> indicating that the cause of orofacial pain is more likely to be bone degeneration of the TMJ</translate>, | :*<math>cr>0</math> <translate><!--T:77--> indicating that the cause of orofacial pain is more likely to be bone degeneration of the TMJ</translate>, | ||
:*<math>cr<0</math> <translate><!--T:78--> which indicates that the cause of orofacial pain is more likely not bone degeneration of the TMJ</translate>. | :*<math>cr<0</math> <translate><!--T:78--> which indicates that the cause of orofacial pain is more likely not bone degeneration of the TMJ</translate>. | ||
<center> | <center> | ||
===<translate><!--T:79--> Second Clinical Approach</translate>=== | ===<translate><!--T:79--> Second Clinical Approach</translate>=== | ||
''(<translate><!--T:80--> hover over the images</translate>)'' | ''(<translate><!--T:80--> hover over the images</translate>)'' | ||
<gallery | |||
<gallery widths="350" heights="282" perrow="2" mode="slideshow"> | |||
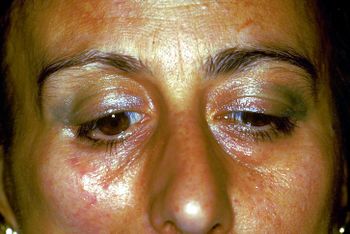
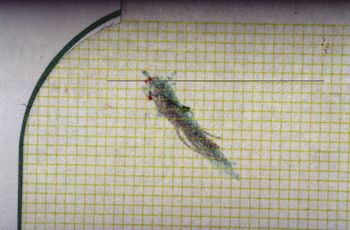
File:Spasmo emimasticatorio.jpg|'''<translate><!--T:81--> Figure</translate> 1:''' <translate><!--T:82--> Patient reporting "Orofacial pain in the right hemilateral"</translate> | File:Spasmo emimasticatorio.jpg|'''<translate><!--T:81--> Figure</translate> 1:''' <translate><!--T:82--> Patient reporting "Orofacial pain in the right hemilateral"</translate> | ||
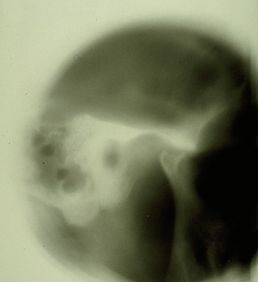
File:Spasmo emimasticatorio ATM.jpg|'''<translate><!--T:83--> Figure</translate> 2:''' <translate><!--T:84--> Patient's TMJ Stratigraphy showing signs of condylar flattening and osteophyte</translate> | File:Spasmo emimasticatorio ATM.jpg|'''<translate><!--T:83--> Figure</translate> 2:''' <translate><!--T:84--> Patient's TMJ Stratigraphy showing signs of condylar flattening and osteophyte</translate> | ||
| Line 197: | Line 199: | ||
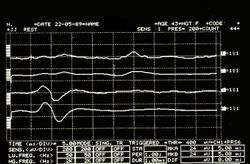
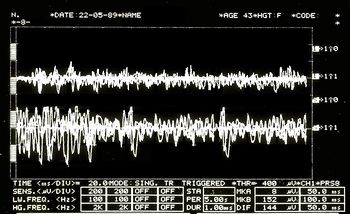
File:EMG2.jpg|'''<translate><!--T:89--> Figure</translate> 5:''' <translate><!--T:90--> EMG Interferential Pattern. Overlapping upper traces corresponding to the right masseter, lower to the left masseter</translate>. | File:EMG2.jpg|'''<translate><!--T:89--> Figure</translate> 5:''' <translate><!--T:90--> EMG Interferential Pattern. Overlapping upper traces corresponding to the right masseter, lower to the left masseter</translate>. | ||
</gallery> | </gallery> | ||
</center> | |||
<br /><translate><!--T:91--> So be it then <math>P(D)</math> the probability of finding, in the sample of our <math>n</math> people, individuals who present the elements belonging to the aforementioned set <math>D=\{\delta_1,\delta_2,...,\delta_n\}</math></translate> | <br /><translate><!--T:91--> So be it then <math>P(D)</math> the probability of finding, in the sample of our <math>n</math> people, individuals who present the elements belonging to the aforementioned set <math>D=\{\delta_1,\delta_2,...,\delta_n\}</math></translate> | ||
| Line 509: | Line 514: | ||
===<translate><!--T:155--> Third Clinical Approach</translate>=== | ===<translate><!--T:155--> Third Clinical Approach</translate>=== | ||
''(<translate><!--T:156--> hover over the images</translate>)'' | ''(<translate><!--T:156--> hover over the images</translate>)'' | ||
< | <center> | ||
<gallery widths="350" heights="282" perrow="2" mode="slideshow"> | |||
File:Spasmo emimasticatorio.jpg|'''<translate><!--T:157--> Figure</translate> 1:''' <translate><!--T:158--> Patient reporting "Orofacial pain in the right hemilateral)</translate> | File:Spasmo emimasticatorio.jpg|'''<translate><!--T:157--> Figure</translate> 1:''' <translate><!--T:158--> Patient reporting "Orofacial pain in the right hemilateral)</translate> | ||
File:Spasmo emimasticatorio ATM.jpg|'''<translate><!--T:159--> Figure</translate> 2:''' <translate><!--T:160--> Patient's TMJ Stratigraphy showing signs of condylar flattening and osteophyte</translate> | File:Spasmo emimasticatorio ATM.jpg|'''<translate><!--T:159--> Figure</translate> 2:''' <translate><!--T:160--> Patient's TMJ Stratigraphy showing signs of condylar flattening and osteophyte</translate> | ||
| Line 520: | Line 525: | ||
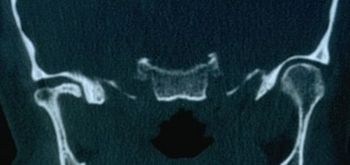
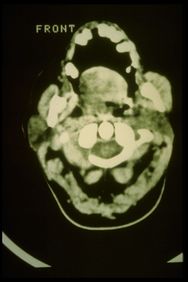
File:Spasmo emimasticatorio TC.jpg|'''<translate><!--T:171--> Figure</translate> 8:''' <translate><!--T:172--> Axial CT of the facial massif in which there is a marked hypertrophy of the right masseter</translate> | File:Spasmo emimasticatorio TC.jpg|'''<translate><!--T:171--> Figure</translate> 8:''' <translate><!--T:172--> Axial CT of the facial massif in which there is a marked hypertrophy of the right masseter</translate> | ||
</gallery> | </gallery> | ||
</center> | |||
</center> | |||
Latest revision as of 01:55, 17 October 2022
In this chapter, we will discuss the logic of language coupled with mathematical probability. We have seen that classical logic alone is insufficient to determine accurate diagnoses; hence, a conceptual and formal overview is given on why probability can be very useful. Providing illustrations of instances of clinical cases, we will see how the logic of probabilistic language is able to provide us a differential diagnosis in a ‘good enough’ way.
The conclusion is that it is possible to demonstrate that, even with the addition of probabilistic reasoning alone, it is not possible to determine exact diagnoses, so other enrichments are being sought for our language.
Probabilistic language logic in medicine
every scientific idea (whether in medicine, architecture, engineering, chemistry, or any other subject), when put into practice, is subject to small errors and uncertainties. Mathematics - through probability theory and statistical inference - helps to precisely control and thereby contain these uncertainties. It always has to be considered that in all practical cases "the outcomes also depend on many other factors external to the theory", whether they be initial and environmental conditions, experimental errors, or something else.
All the uncertainties about these factors make the theory–observation relationship a probabilistic one. In the medical approach, there are two types of uncertainty that weigh the most on diagnoses: subjective uncertainty and casuality.[1][2]
It becomes essential, therefore, in this scenario to distinguish between these two uncertainties and to show that the concept of probability has different meanings in these two contexts.
We will try to expose these concepts by linking each crucial step to the clinical approach that has been reported in the previous chapters and in particular the approach in the dental and neurological context in contending for the primacy of the diagnosis for our dear Mary Poppins.
Subjective uncertainty and casuality
Let us imagine asking Mary Poppins which of the two medical colleagues — the dentist or the neurologist — is right.
The question would create a kind of agitation based on inner uncertainty; therefore, the notions of certainty and uncertainty refer to subjective epistemic states of human beings and not to states of the external world, because there is no certainty or uncertainty in that world. In this sense, as we have mentioned, there are an inner world and a world outside ourselves that both do not respond to canons of uncertainty, yet of probability.
Mary Poppins may be subjectively certain or uncertain as to whether she is suffering from TMDs or a neuropathic or neuromuscular form of OP: this because "uncertainty" is a subjective, epistemic state below the threshold of knowledge and belief; hence the term.
Subjective uncertainty
Without a doubt the term ‘subjective’ scares many, especially those who intend to practice science by pursuing the healthy ideal of ‘objectivity’, as this term is perceived by common sense. It is, therefore, appropriate to make some clarifications on the use of this term in this context:
- ‘Subjective’ indicates that the probability assessment depends on the information status of the individual who performs it.
- ‘Subjective’ does not mean arbitrary.
The so-called ‘objectivity’, as perceived by those outside scientific research, is defined when a community of rational beings shares the same state of information. But even in this case, one should speak more properly of ‘intersubjectivity’ (i.e. the sharing, by a group, of subjective opinions).
In clinical cases — precisely because patients rarely possess advanced notions of medicine — subjective uncertainty must be considered. Living with uncertainty requires us to use a probabilistic approach.
Casuality
The casuality indicates the lack of a certain connection between cause and effect. The uncertainty of a close union between the source and the phenomenon is among the most adverse problems in determining a diagnosis.
In a clinical case a phenomenon (such as for example a malocclusion, a crossbite, an openbite, etc ...) is randomly associated with another phenomenon (such as TMJ bone degeneration); when there are exceptions for which the logical proposition it's not always true (but it is most of the time), we will say that the relation is not always true but it is probable.
Subjective and objective probability
In this chapter, some topics already treated in the fantastic book by Kazem Sadegh-Zadeh[3], who tackles the problem of the logic of medical language, are taken up again and we reshape their content by referring them to our clinical case of Mary Poppins, to keep our understanding closer to dental contexts.
Random and subjectively uncertain events are said to be probable; consequently, casuality and uncertainty are treated as qualitative, comparative or quantitative probabilities.
To clarify this concept, let us go back to the example of Mary Poppins. A doctor, having heard her symptoms will be able to say that:
- Mary Poppins is probably suffering from TMDs (qualitative term).
- Mary Poppins is more likely to have TMDs than neuropathic OP (comparative term: number of diagnosed cases of TMDs versus nOP.
- The probability that Mary Poppins has TMDs is 0.15 (quantitative term, relative to the population).
Subjective probability
In a context of human subjective uncertainty, the probabilistic, qualitative, comparative and/or quantitative data can be interpreted as a measure of subjective uncertainty by the clinician, in order to make the 'states of conviction' numerically representable.
For example, saying that "the probability that Mary Poppins is affected by TMDs is 0.15 of the cases" is the same as saying "in the measure of 15%, I believe that Mary Poppins is affected by TMDs"; which means that the degree of conviction is the degree of subjective probability.
Objective probability
On the other hand, events and random processes cannot be described by deterministic processes in the form 'if A then B'. Statistics are used to quantify the frequency of association between A and B and to represent the relationships between them as a degree of probability that introduces the degree of objective probability.
In the wake of the growing probabilization of uncertainty and randomness in medicine since the eighteenth century, the term "probability" has become a respected element of medical language, methodology and epistemology.
Unfortunately, the two types of probability, the subjective probability and the objective one, are not accurately differentiated in medicine, and the same happens in other disciplines too. The fundamental fact remains that the most important meaning that probability theory has generated in medicine, particularly in the concepts of probability in aetiology, epidemiology, diagnostics and therapy, is its contribution to our understanding and representation of biological casuality.
Probabilistic-causal analysis
From these premises it is clear that the clinical diagnosis is made using the so-called hypothetical-deductive method referred to as DN[4] (deductive-nomological model[5]). But this is not realistic, since the medical knowledge used in clinical decision-making hardly contains causal deterministic laws to allow causal explanations and, hence, to formulate clinical diagnoses, among other things in the specialist context. Let us try to analyse again the case of our Mary Poppins, this time trying a probabilistic-causal approach.
Let us consider a number of individuals including people who report Orofacial Pain who generally have bone degeneration of the Temporomandibular Joint. However, there may also be other apparently unrelated causes. We must mathematically translate the 'relevance' that these causal uncertainties have in determining a diagnosis.
The casual relevance
To do this we consider the degree of causal relevance of an event with respect to an event where:
- = patients with bone degeneration of the temporomandibular joint.
- = patients reporting orofacial pain.
- = patients without bone degeneration of the temporomandibular joint.
We will use the conditional probability , that is the probability that the event occurs only after the event has already occurred.
With these premises the causal relevance of the sample of patients is:
where
- indicates the probability that some people (among taken into consideration) suffer from Orofacial Pain caused by bone degeneration of the Temporomandibular Joint,
while
- indicates the probability that other people (always among taken into consideration) suffer from Orofacial Pain conditioned by something other than bone degeneration of the Temporomandibular Joint.
Since all probability suggest that is a value between and , the parameter will be a number that is between and .
The meanings that we can give to this number are as follows:
- we have the extreme cases (which in reality never occur) which are:
- indicating that the only cause of orofacial pain is bone degeneration of the TMJ,
- which indicates that the cause of orofacial pain is never bone degeneration of the TMJ but is something else,
- indicating that the probability that orofacial pain is caused by bone degeneration of the TMJ or otherwise is exactly the same,
- and the intermediate cases (which are the realistic ones)
- indicating that the cause of orofacial pain is more likely to be bone degeneration of the TMJ,
- which indicates that the cause of orofacial pain is more likely not bone degeneration of the TMJ.
Second Clinical Approach
(hover over the images)
So be it then the probability of finding, in the sample of our people, individuals who present the elements belonging to the aforementioned set
In order to take advantage of the information provided by this dataset, the concept of partition of causal relevance is introduced:
The partition of causal relevance
- Always be the number of people we have to conduct the analyses upon, if we divide (based on certain conditions as explained below) this group into subsets with , a cluster is created that is called a "partition set" :
where with the symbolism it indicates that the subclass is contained in .
The partition , in order for it to be defined as a partition of causal relevance, must have these properties:
- For each subclass the condition must apply ie the probability of finding in the subgroup a person who has the symptoms, clinical signs and elements belonging to the set . A causally relevant partition of this type is said to be homogeneous.
- Each subset must be 'elementary', i.e. it must not be further divided into other subsets, because if these existed they would have no causal relevance.
Now let us assume, for example, that the population sample , to which our good patient Mary Poppins belongs, is a category of subjects aged 20 to 70. We also assume that in this population we have those who present the elements belonging to the data set which correspond to the laboratory tests mentioned above and precisa in 'The logic of classical language'.
Let us suppose that in a sample of 10,000 subjects from 20 to 70 we will have an incidence of 30 subjects showing clinical signs and . We preferred to use these reports for the demonstration of the probabilistic process because in the literature the data regarding clinical signs and symptoms for Temporomandibular Disorders have too wide a variation as well as too high an incidence in our opinion.[6][7][8][9][10][11]
An example of a partition with presumed probability in which TMJ degeneration (Deg.TMJ) occurs in conjunction with Temporomandibular Disorders (TMDs) would be the following:
| where | |||||
| where | |||||
| where | |||||
| where |
Clinical situations
These conditional probabilities demonstrate that each of the partition's four subclasses is causally relevant to patient data in the population sample . Given the aforementioned partition of the reference class, we have the following clinical situations:
- Mary Poppins degeneration of the temporomandibular joint Temporomandibular Disorders
- Mary Poppins degeneration of the temporomandibular joint no Temporomandibular Disorders
- Mary Poppins no degeneration of the temporomandibular joint Temporomandibular Disorders
- Mary Poppins no degeneration of the temporomandibular joint no Temporomandibular Disorders
To arrive at the final diagnosis above, we conducted a probabilistic-causal analysis of Mary Poppins' health status whose initial data were .
In general, we can refer to a logical process in which we examine the following elements:
- an individual:
- its initial data set
- a population sample to which it belongs,
- a base probability
At this point we should introduce too specialized arguments that would take the reader off the topic but that have an high epistemic importance for which we will try to extract the most described logical thread of the Analysandum/Analysans concept.
The probabilistic-causal analysis of is then a couple of the following logical forms (Analysandum / Analysans[12]):
- Analysandum : is a logical form that contains two parameters: probability to select a person who has the symptoms and elements belonging to the set , and the generic individual who is prone to those symptoms.
- Analysan : is a logical form that contains three parameters: the partition , the generic individual belonging to the population sample and (Knowledge Base) which includes a set of statements of conditioned probability.
For example, it can be concluded that the definitive diagnosis is the following:
- this means that our Mary Poppins is 95% affected by TMDs, since she has a degeneration of the Temporomandibular Joint in addition to the positive data
Final considerations
We took a long and tortuous path to better understand the complexity encountered by the colleague struggling with the very heavy ethical responsibility of making a diagnosis. However, this task becomes even more complex when we need to be detailed and careful in making a differential diagnosis.
Here, we enter a delicate topic, that is connected with the epistemological contents and that first of all was reported in the "Introduction". We are talking about:
- Interdisciplinarity:
In science policy, it is generally recognized that science-based problem solving requires interdisciplinary research (IDR), as proposed by the EU project called Horizon 2020[13]. In a recent study, the authors focus on the question why researchers have cognitive and epistemic difficulties in conducting IDR. It is believed that the loss of philosophical interest in the epistemology of interdisciplinary research is caused by a philosophical paradigm of science called "Physics Paradigm of Science", which prevents recognition of important IDR changes in both the philosophy of science and research.
The proposed alternative philosophical paradigm, called 'Engineering Paradigm of Science', makes alternative philosophical assumptions about aspects such as the purpose of science, the character of knowledge, the epistemic and pragmatic criteria for the acceptance of knowledge and the role of technological tools. Consequently, scientific researchers need so-called metacognitive scaffolds to assist them in the analysis and reconstruction of how 'knowledge' is constructed in different disciplines.
In interdisciplinary research, metacognitive scaffolds help interdisciplinary communication analyse and articulate how the discipline builds knowledge[14][15]
This concept is linked to the previously discussed topic in which the colleague should be aware of his own 'Subjective Uncertainty' (due to a classic logic language 'sick or healthy') and of 'Objective Uncertainty' (due to a probabilistic logic language 'probably sick or probably healthy'). It is not complicated to prove this assertion: the uncertainty we are talking about derives from the fact that the elements, assertions, data, classes and subclasses mentioned and that build the apparatus of the logic of probabilistic's language: Analysandum and Analysan are elements that exist in a specific world, and in this case in a dental context in which the element of the process indisputably indicates a "basic knowledge" only in a specific dental context.
This conclusion confirmed by the dentist was the following:
or better: it is my 95% belief that Mary Poppins is affected by TMDs since she has a degeneration of the temporomandibular joint in addition to the positivity of the data
But something strange happens because out of nowhere, a researcher, who uses 'metacognitive scaffolds'[16] for an implementation in the analysis and reconstruction of how 'knowledge' is built in different disciplines, demands an answer to the following question from the dentist:
«...is there another world or context, parallel to yours, in which in addition to the D data there are further data unknown to you?»
|
and increase the dose: submit Mary Poppins to the following trigeminal electrophysiological tests, label them as we did previously for the set data generating another set containing a number of unknown data (not belonging to the purely dental branch) thereby creating an entirely new set that we will call (called precisely due to the presence of data unknown to the dental context).
Positive radiological report of the TMJ in Figure 2
Positive CT report of the TMJ in Figure 3
Positive axiographic report of the condylar traces in Figure 4
Asymmetric EMG interference pattern in Figure 5
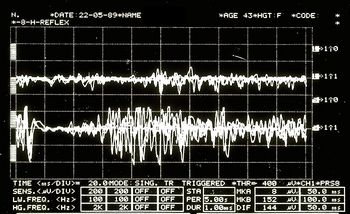
Jaw jerk in Figure 6
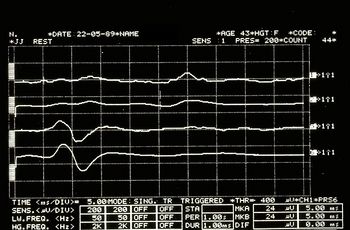
Mechanical Silent Period in Figure 7
CT right masseter muscle in Figure 8
Third Clinical Approach
(hover over the images)
In this way it has been shown that, inevitably,
By exploring this perimeter line of the specialist context, we will create an area close to it which we will call the 'fuzzy zone' or 'fuzzy logic' which we will discuss in the next chapter.
«... from what it seems not even with a probabilistic language logic we will be able to define an exact diagnosis.»
(in fact, for this reason we should also consider Fuzzy Logic Language) |
- ↑ Vázquez-Delgado E, Cascos-Romero J, Gay-Escoda C, «Myofascial pain associated to trigger points: a literature review. Part 2: differential diagnosis and treatment», in Med Oral Patol Oral Cir Bucal, 2007».
PMID:20173729
DOI:10.4317/medoral.15.e639 - ↑ Thoppay J, Desai B, «Oral burning: local and systemic connection for a patient-centric approach», in EPMA J, 2019».
PMID:30984309 - PMCID:PMC6459460
DOI:10.1007/s13167-018-0157-3 - ↑ Sadegh-Zadeh Kazem, «Handbook of Analytic Philosophy of Medicine», Springer, 2012, Dordrecht».
ISBN: 978-94-007-2259-0
DOI:10.1007/978-94-007-2260-6 . - ↑ Sarkar S, «Nagel on Reduction», in Stud Hist Philos Sci, 2015».
PMID:26386529
DOI:10.1016/j.shpsa.2015.05.006 - ↑ DN model of scientific explanation, also known as Hempel's model, Hempel–Oppenheim model, Popper–Hempel model, or covering law model
- ↑ Pantoja LLQ, De Toledo IP, Pupo YM, Porporatti AL, De Luca Canto G, Zwir LF, Guerra ENS, «Prevalence of degenerative joint disease of the temporomandibular joint: a systematic review», in Clin Oral Investig, 2019».
PMID:30311063
DOI:10.1007/s00784-018-2664-y - ↑ De Toledo IP, Stefani FM, Porporatti AL, Mezzomo LA, Peres MA, Flores-Mir C, De Luca Canto G, «Prevalence of otologic signs and symptoms in adult patients with temporomandibular disorders: a systematic review and meta-analysis», in Clin Oral Investig, 2017».
PMID:27511214
DOI:10.1007/s00784-016-1926-9 - ↑ Bonotto D, Penteado CA, Namba EL, Cunali PA, Rached RN, Azevedo-Alanis LR, «Prevalence of temporomandibular disorders in rugby players», in Gen Dent».
PMID:31355769 - ↑ da Silva CG, Pachêco-Pereira C, Porporatti AL, Savi MG, Peres MA, Flores-Mir C, De Luca Canto G, «Prevalence of clinical signs of intra-articular temporomandibular disorders in children and adolescents: A systematic review and meta-analysis», in Am Dent Assoc, 2016». - PMCID:26552334
DOI:10.1016/j.adaj.2015.07.017 - ↑ Gauer RL, Semidey MJ, «Diagnosis and treatment of temporomandibular disorders», in Am Fam Physician, 2015».
PMID:25822556 - ↑ Kohlmann T, «Epidemiology of orofacial pain», in Schmerz, 2002».
PMID:12235497
DOI:10.1007/s004820200000 - ↑ Westmeyer H, «The diagnostic process as a statistical-causal analysis», in APA, 1975».
DOI:10.1007/BF00139821
This is an Open Access resource! - ↑ European Union, Horizon 2020
- ↑ Boon M, Van Baalen S, «Epistemology for interdisciplinary research - shifting philosophical paradigms of science», in Eur J Philos Sci, 2019».
DOI:10.1007/s13194-018-0242-4 9(1):16. - ↑ Boon M, «An engineering paradigm in the biomedical sciences: Knowledge as epistemic tool», in Prog Biophys Mol Biol, 2017».
DOI:10.1016/j.pbiomolbio.2017.04.001 - ↑ Boon M, Van Baalen S, «Epistemology for interdisciplinary research - shifting philosophical paradigms of science», in Eur J Philos Sci, 2019».
PMID:30873248 - PMCID:PMC6383598
DOI:10.1007/s13194-018-0242-4
This is an Open Access resource!
particularly focusing on the field of the neurophysiology of the masticatory system